how does a crown court work
These booklets are available from the ABA to provide a brief overview different aspects of the justice system. Cases referred to them for trial by a Magistrates Court because the offence is indictable.
Confiscation proceedings are heard in the Crown Court after a person has been convicted of a crime which involves either financial gain an attempt to gain financially or the laundering of.

. Cases sent for trial by magistrates courts because the offences are indictable only ie. Wales and Chester with Cardiff as the centre. Midland and Oxford Birmingham.
Brightside Online Mentoring puts young people in touch with mentors who can help them with their education and career options. Crown prosecutors mustin a timely fashionprovide disclosure the reasons for the charge and the evidence against the accused to the accused so that the accused can fully respond to the charges against them. Normally has a jury - which decides if youre guilty or not.
The Crown Court breaks down offences into three classes depending on the seriousness of the crime. These often take place with significant offences which the Magistrates Court does not have the powers to handle. Following Allocation to the Crown Court.
Your legal adviser should instruct a barrister counsel to draft the indictment a copy of which you should receive and check for accuracy. This class covers the most serious offences such as treason and murder. However for some purposes the Crown Court is hierarchically subordinate to the High Court and its Divisional Courts.
Again appeals will go to the High Court and then to the Court of Appeal although to different divisions of those courts. The Crown Court breaks down offences into three classes depending on the seriousness of the crime. Law the Courts Vol 2.
The accuseds lawyers defence counsel and Crown prosecutors are equal contributors and advocates of justice Crown prosecutors cannot. The court is open to the public. The Crown Prosecutor will present their case to the court by calling witnesses and examining them directly while they are under oath.
The tribunals system has its own structure for. This class includes offences such. Law the Courts Vol 3.
The Role of the Courts. Civil cases will sometimes be dealt with by magistrates but may well go to a county court. Those which can only be heard by the Crown Court.
In superior court the two major types of court cases are criminal and civil. It deals with serious criminal cases which include. Department of Labor DOL common court clerk responsibilities include.
Appeals from the Crown Court will go to the High Court and potentially to the Court of Appeal or even the Supreme Court. The Crown Court unlike the magistrates courts it is a single entity sits in 71 court centres across England and Wales. Has a judge - who decides what sentence you get.
The Crown Court of England and Wales is together with the High Court of Justice and the Court of Appeal one of the constituent parts of the Senior Courts of England and Wales. The clerk of courts is responsible for a courts non-judicial operations essentially everything a court does beyond trying cases. The Crown Court must receive the indictment from you within 28 days of the sending of the case unless an extension of time has been granted.
The Crown Court deals with the most serious criminal cases such as murder and rape. If you plead not guilty at the plea and trial preparation hearing the trial will be set to take place in front of a judge and jury in Crown Court. If the defendant is found guilty the judge will decide the length of the sentence.
County Courts are the civil counterpart from Crown Courts. If youre facing a criminal. The different types of court - magistrates court Crown Court and youth court - the crimes they deal with and the level of sentences they can give.
Crown Court is a venue where serious criminal cases are tried. Bright Knowledge is here to help you work out what you want to achieve and how you can get there. Our court system in England and Wales is complicated.
Preparing and issuing orders of the court summonses probation orders other official documentation Preparing dockets. A Crown Court will either hear appeals form Magistrates Courts sentence criminals from magistrates or hold trials themselves. Your solicitor if you have one can explain what happens in court.
Crown Court is where the most serious offences are heard and these can include either way or indictable only offences. The law presumes an accused person is innocent until proved guilty beyond reasonable doubt by the prosecution. The Crown Court will deal with more serious criminal cases including.
The Crown Court is more formal than magistrates courts for example the judge wears a gown and wig. Law the Courts Vol 1. They often have a jury.
Southeastern with London as the administrative centre. The Crown Court sits in. What is the Crown Court.
Which cases are heard in a certain court can be confusing. Cases referred to them for trial by a Magistrates Court because the offence is indictable. As well as mentoring support the website provides loads of fun and fascinating resources about university careers.
Once all evidence has been heard the jury will make their decision and the judge will designate the. Occasionally these courts can also hear matters being appealed from the Magistrates Courts. Essentially you have the magistrates court at the bottom end of the scale then the Crown Court all the way up to the High Court Court of Appeal and finally the Supreme Court.
The judge decides questions of law sums up the case to the jury and sentences or discharges the accused. The Crown Court includes a jury of 12 members of the public who decide whether youre guilty or not guilty. In the magistrates court there are no juries.
The Crown Court tries those criminal matters where the defendant has elected trial on an either-way offence or where the matter is indictable only so serious that they can only be tried in a Crown Court. A Crown Court will either hear appeals form Magistrates Courts sentence criminals from magistrates or hold trials themselves. It is the highest court of first instance in criminal cases.
The Crown Court hears trials on indictment as well as sentencings and appeals from the magistrates courts. The first witness will be called sworn in or affirmed and then the direct examination would commence with. There are six court circuits.
Either way offences those that can be heard by either court but where the defendant opts to have the case heard in.

Sheffield Crown Court Courtroom 2 South Yorkshire Court Sheffield
Uk Court Structure Justcite Knowledge Base

Our Keen Lawyers In Yr9 Worked Alongside Our Law Students M Khanom And A Shan Took Part In The Regional Heat Mock Tria Law Student Wolverhampton Competing

Law Reports Oxford Law Faculty

Lancaster Crown Court The Oldest Working Courtroom In Britain Old Things Courtroom Lancashire

Pin On Hs Design Annapolis Client On The Court

Your Countries Courts Skyscrapercity Courtroom Things To Do In London Law And Justice

Henry Viii The Anglophile Henry Viii Tudor History History
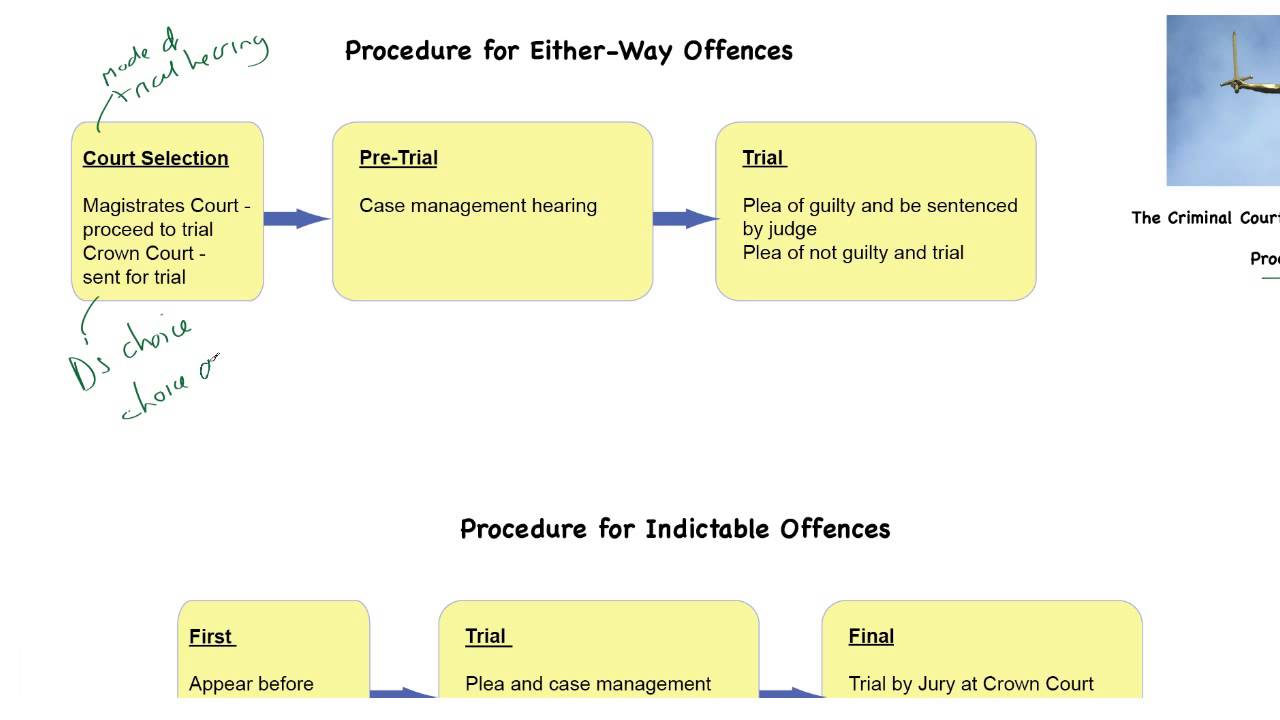
Criminal Court Process Procedure To Trial Via The Law Bank Case Management Criminal Procedure Court

Pin By Antonia Mautner On Rigoletto In 2021 Sheffield South Yorkshire Court

Scaffolder Killed In Fall Fitting Guardrails On Fragile Roof Administration How To Plan Development
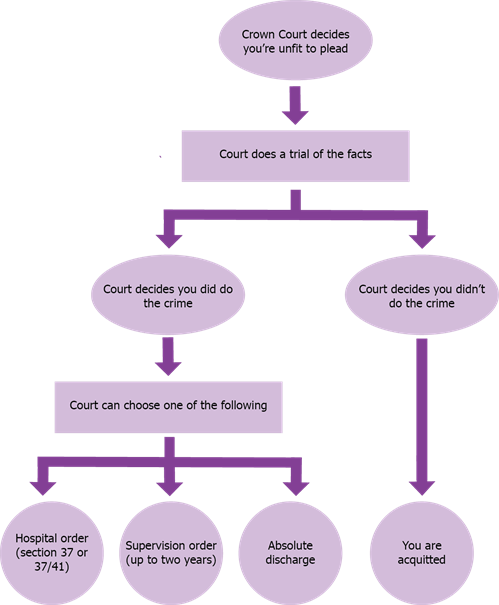
Criminal Charges Pleading Guilty Or Not Guilty Mind

Judicial Authority United Kingdom Legal Research Guide Guides At Georgetown Law Library

The First Hearing In The Crown Court The Plea And Trial Preparation Hearing The Crown Prosecution Service
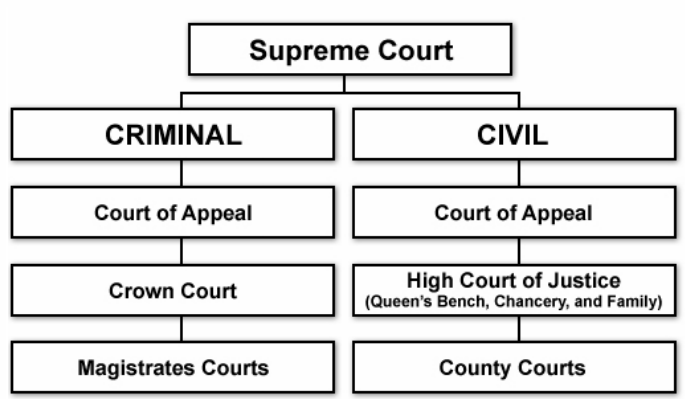
Court Structure In England And Wales 1446 Words Essay Example

Court Process In The Magistrates Court Victims Of Crime Victoria

Central Criminal Court Of England And Wales The Old Bailey Court No 1 Wales England England Wales

Court Process In The Magistrates Court Victims Of Crime Victoria

Crown Court In Lincoln Castle Uk Built By William The Conqueror In The 11th Century Taken From The Main Gate Loo Lincoln England Lincoln Castle Wales England
